Global Citizenship: Understanding Shared Human Values
Global citizenship encompasses the idea that individuals are members of a broader global community, transcending national and geographical boundaries. It involves understanding and upholding shared human values, promoting peace, sustainability, and respect for diversity. This perspective encourages individuals to recognize their interconnectedness with people and the planet, fostering a sense of responsibility towards global challenges and opportunities. Embracing global citizenship means engaging with the world with an open mind, appreciating different cultures, and contributing to a more inclusive and equitable society for all.
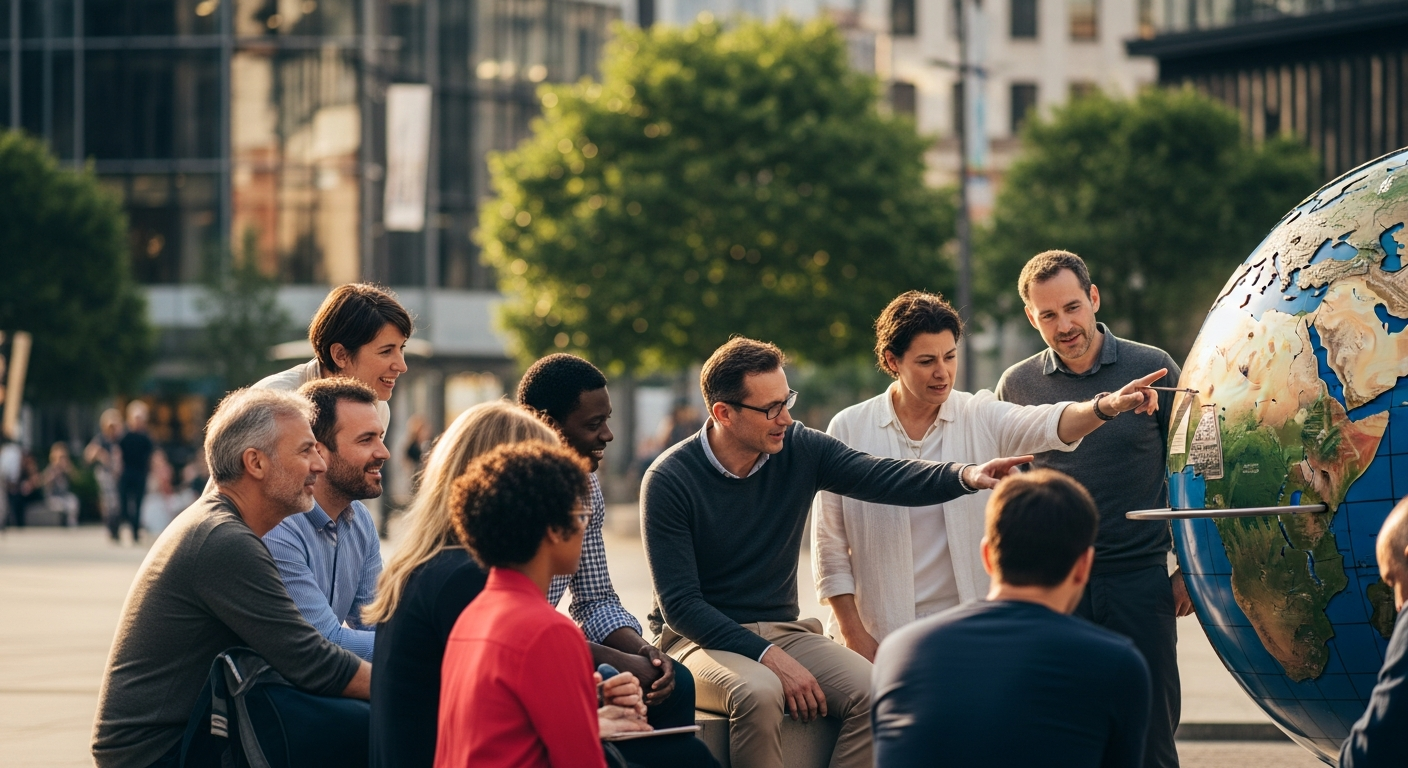

What is Global Citizenship in Modern Society?
Global citizenship represents a framework for understanding one’s role in an interconnected world. It extends beyond national identity, encouraging individuals to see themselves as part of a larger humanity. In modern society, this concept is increasingly relevant due to globalization, digital communication, and shared challenges like climate change and economic interdependence. Embracing global citizenship involves recognizing universal human rights, promoting social justice, and actively participating in efforts to create a peaceful and sustainable world. This perspective emphasizes empathy, critical thinking, and a commitment to collective well-being, fostering a sense of responsibility for the planet and its inhabitants.
Exploring Shared Values Across Diverse Cultures and Communities
Despite the vast array of cultures and communities worldwide, certain fundamental shared human values often emerge as common threads. These include principles such as respect, compassion, justice, honesty, and the pursuit of peace. While the expression and prioritization of these values may vary across different cultural contexts, their underlying essence resonates universally. Understanding these shared values is crucial for fostering cross-cultural dialogue and building bridges between diverse groups. Recognizing common ground can help mitigate misunderstandings and promote greater cohesion, reinforcing the idea that humanity, at its core, shares many aspirations for a dignified and fulfilling life.
How Do Social Interactions Shape Human Behavior and Identity?
Social interactions are foundational in shaping both individual human behavior and collective identity. From early childhood, our interactions with family, friends, and broader society influence our beliefs, attitudes, and actions. These interactions provide the context for learning social norms, developing communication skills, and forming a sense of self. Through reciprocal exchanges, individuals internalize cultural expectations and societal structures, which in turn inform their worldview and sense of belonging. The dynamic interplay of various social groups and their interactions contributes to the continuous evolution of both personal and collective identities within a community.
Understanding Demographic Trends and Group Structures
Demographic trends, such as population growth, aging populations, and migration patterns, significantly impact the structures and dynamics of human groups. Analyzing these trends helps in understanding societal shifts, resource allocation, and the changing composition of communities. Different group structures, ranging from families and local associations to national and international organizations, emerge in response to various social, economic, and cultural factors. These structures provide frameworks for cooperation, governance, and the transmission of culture, influencing how individuals interact and how resources are distributed within a given society. Understanding these elements is vital for effective social planning and policy development.
Fostering Cohesion and Positive Relationships in a Global Context
Fostering social cohesion and positive relationships is essential for the well-being of any community, especially in an increasingly globalized world. This involves promoting mutual understanding, tolerance, and empathy among people from different backgrounds. Initiatives that encourage cross-cultural exchange, collaborative projects, and inclusive practices can strengthen bonds and reduce prejudice. Creating environments where diverse perspectives are valued and respected helps to build trust and cooperation. Ultimately, strong, positive relationships, both locally and globally, contribute to more resilient and harmonious societies capable of addressing shared challenges collectively.
The Evolution of Human Norms in Urban and Rural Settings
Human norms, which are unwritten rules of behavior, continuously evolve, often influenced by the specific environments in which people live. Urban and rural settings, for example, frequently exhibit distinct normative frameworks. Urban areas, characterized by high population density, diversity, and rapid change, often see norms that emphasize individualism, efficiency, and adaptability. In contrast, rural settings may retain norms that prioritize community interdependence, tradition, and slower paces of life. However, with increased connectivity and migration, there is often an intermingling and adaptation of norms between these settings, leading to a dynamic evolution of social expectations across the entire spectrum of human settlement. This ongoing adaptation reflects broader societal trends and the changing needs of populations.
Global citizenship encourages a broader perspective on humanity, recognizing the intricate web of connections that link individuals, communities, and nations. By understanding shared values, appreciating cultural diversity, and acknowledging the impact of social structures and demographic shifts, individuals can contribute to a more interconnected and responsible world. This involves cultivating empathy, engaging in thoughtful interactions, and actively participating in efforts that promote peace, sustainability, and equity for all members of the global community.