Modular design principles in electronic gadgets
Modular design in electronic gadgets involves constructing devices from independent, interchangeable components. This approach allows for greater flexibility in manufacturing, easier repairs, and potential for upgrades, moving away from monolithic designs where components are tightly integrated and often irreplaceable. Understanding these principles reveals how modern electronics are evolving towards more adaptable and sustainable forms.
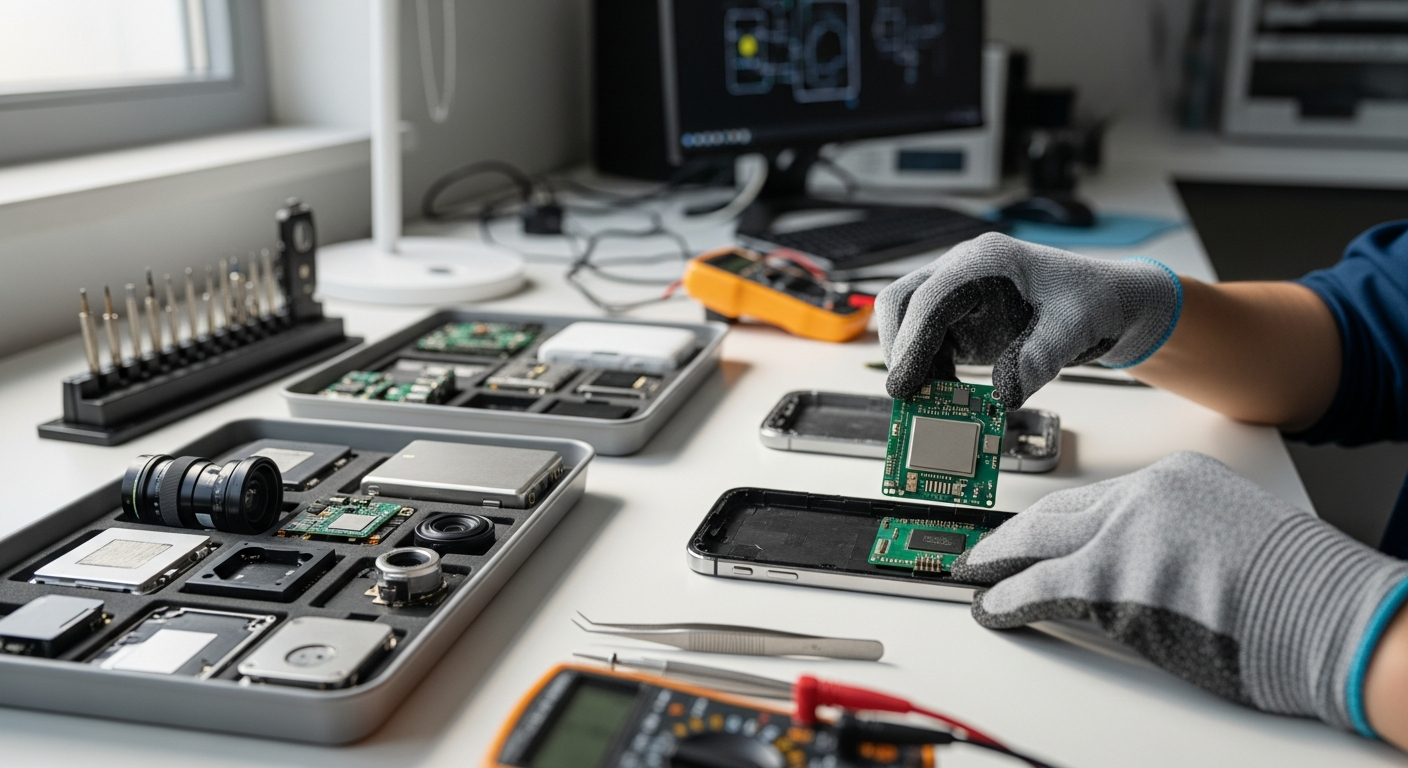

Modular design is fundamentally changing how electronic gadgets are conceived, developed, and maintained. By breaking down complex systems into smaller, self-contained units, manufacturers can streamline production processes, reduce waste, and extend the functional life of devices. This paradigm shift offers significant advantages for both producers and consumers, fostering innovation and promoting a more sustainable approach to technology.
Understanding Modular Hardware Components
At the core of modular design is the ability to treat various hardware elements as distinct components. For instance, the processor, memory, and storage in a device can be designed as individual modules rather than being permanently soldered onto a single circuit board. This allows for easier assembly and, crucially, simplifies the process of replacing or upgrading specific parts. A modular approach enables a system to be configured with different capabilities, catering to diverse user needs without requiring a complete redesign of the entire gadget. Each chip and component is integrated in a way that allows it to function effectively within its module, interacting with other modules through standardized interface protocols.
Benefits for Device Design and Technology
Embracing modularity brings numerous benefits to device design and overall technology advancement. Manufacturers can achieve greater economies of scale by standardizing modules that can be used across multiple product lines. This reduces development costs and speeds up time-to-market for new gadgets. From a digital computing perspective, modularity facilitates experimentation and rapid prototyping. Developers can easily swap out different processor or memory configurations to test performance, optimize data flow, or integrate new functionalities without overhauling the entire system architecture. This flexibility is vital in a fast-evolving industry, enabling quicker adoption of new chip designs and component improvements.
Enhancing User Experience and System Longevity
For end-users, modular design translates into enhanced user experience and significantly extended system longevity. Imagine being able to upgrade your gadget's display to a higher resolution, replace a worn-out battery, or improve its storage capacity without needing to purchase an entirely new device. This not only saves money but also reduces electronic waste, contributing to environmental sustainability. The interface between modules is designed for straightforward interaction, often allowing users or service technicians to perform repairs or upgrades with minimal specialized tools, thereby making technology more accessible and repairable.
Modular Design in Network and Sensor Integration
Modular principles also extend to specialized functionalities like network connectivity and sensor integration. A device might feature interchangeable network modules, allowing users to switch between different cellular technology standards (e.g., 4G to 5G) or even add satellite communication capabilities. Similarly, sensor modules, such as those for environmental monitoring or advanced biometrics, can be integrated or updated independently. This flexibility ensures that gadgets can adapt to evolving data collection needs and network infrastructure, maintaining relevance and functionality over a longer period. The independent nature of these components simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance, as issues can often be isolated to a single module.
Challenges and Future Prospects of Modular Systems
While the advantages are clear, implementing modular design on a wide scale presents certain challenges. Standardization across different manufacturers is crucial for true interoperability, yet achieving industry-wide consensus can be complex. There are also engineering hurdles related to ensuring seamless data transfer and power management between disparate modules. However, the future prospects for modular systems are promising. As technology advances, particularly in areas like smart gadgets and the Internet of Things, the demand for adaptable, repairable, and sustainable device architectures is growing. Continued innovation in chip design, interface protocols, and advanced component manufacturing will likely overcome current limitations, leading to a new generation of highly customizable and long-lasting electronics.
Modular design principles offer a transformative path for the electronics industry, promoting adaptability, sustainability, and user empowerment. By focusing on independent, interchangeable components like processor, memory, storage, display, sensor, network, battery, and interface, manufacturers can create more resilient gadgets that evolve with user needs and technological advancements. This approach signifies a move towards a more flexible and responsible future for digital computing and technology as a whole.